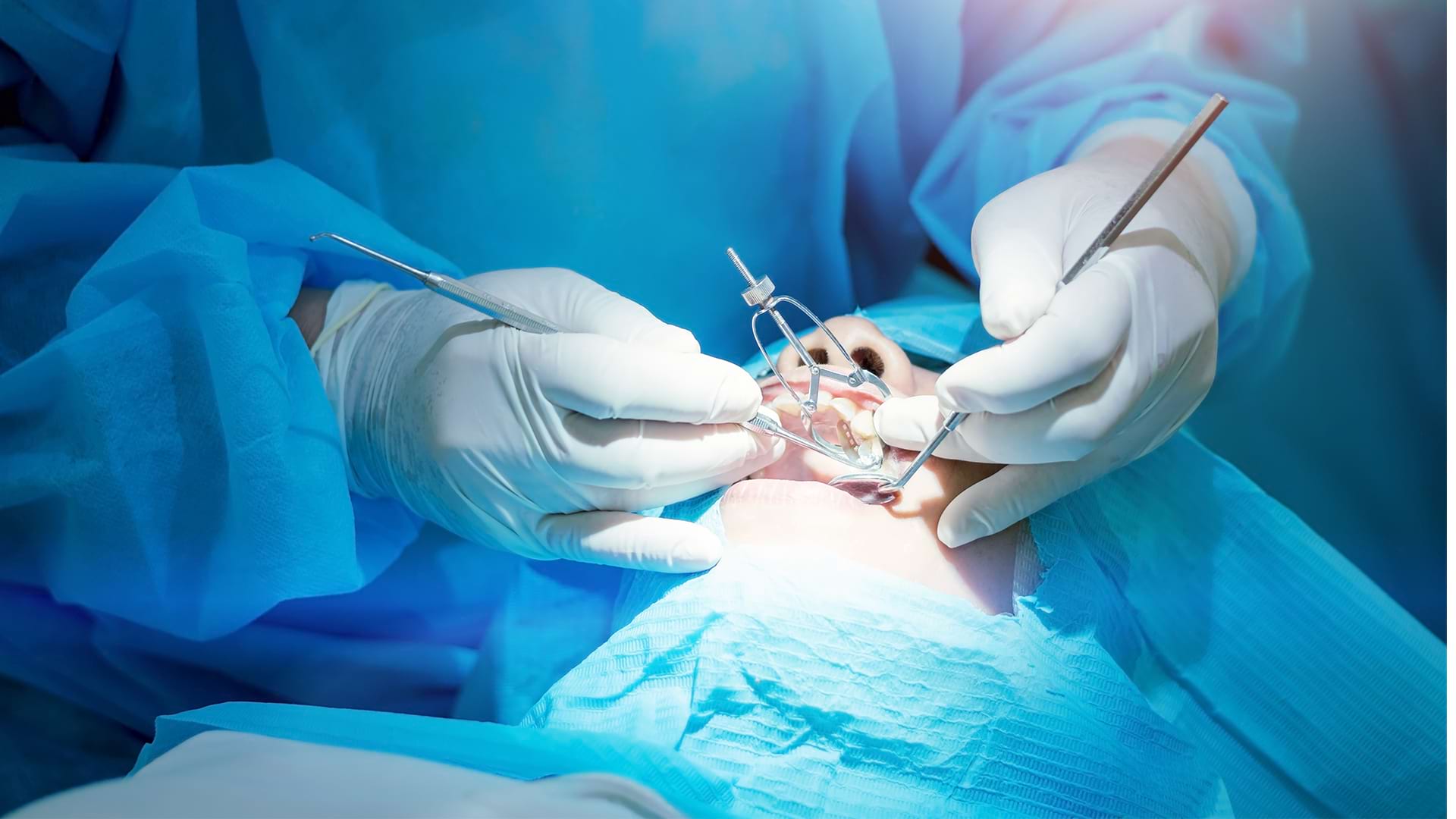
Periodontal Surgery
Gingival surgery (periodontal surgery) is a specialized procedure designed to address deep-seated
issues
within the gums and supporting bone structure.
The Purpose of Periodontal Surgery
- Restoring soft tissues lost due to
periodontal disease.
- Preventing potential tooth loss.
- Eliminating infection-causing
bacteria.
- Reshaping the gum form for better
esthetics and health.
- Performing advanced procedures like
tissue transplants.
Performing Periodontal Surgery
Periodontal surgery is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It is carefully planned based on the degree of
periodontitis, bone loss, or gingival recession.
- Plaque
Removal:
Prior to surgery, oral hygiene must be at its highest level.
- Bacterial
Control:
Strict hygiene prevents bacteria buildup after the procedure.
- Specialist
Care:
A periodontologist is required to plan and oversee the surgery.
Periodontal Surgery Types
Advancements in the past 40 years have brought sophisticated surgical procedures to modern dentistry.
The choice of method depends on the patient's specific needs.
- Soft tissue transfers
- Flap operations
- Guided tissue regeneration
- Depigmentation
Get
a Consultation for Detailed Information:
Patient Assessment Before Surgery
- Evaluation of the patient's
medical history.
- Screening for lesions or
abscesses in the surgical area.
- Analyzing the overall state of
the jaws and gums.
- Detailed explanation of all
risks and benefits.
- Obtaining informed consent
after
meeting all prerequisites.
The Surgical Stage
Gingival operations typically last between 30 and 90 minutes. For patient comfort, procedures are
performed
under local anesthesia, with sedation or general anesthesia options available if required.
Sterilization is paramount. We use disposable sterile gowns, drapes, and equipment to ensure a
microbe-free environment. Preparation is handled with meticulous care to minimize any infection risks.
The procedure begins with small incisions to gently move the gingiva and expose the root surface. This
allows for detailed cleaning and flattening before the restorative phase.
If the procedure involves the gum and nearby bone, the tissue is closed using specialized suturing
techniques. In the case of a gingival transplant, healthy tissue is transferred from a donor area to the
recipient site.
Sutures are typically removed after 7 to 10 days during a follow-up appointment to monitor the healing
progress.
Post-Operative Care
For an optimal and healthy recovery, please follow these guidelines:
- Use prescribed
painkillers
and antiseptic mouthwashes as directed.
- Maintain meticulous
hygiene
in the surgical area.
- Strictly avoid smoking,
as
nicotine significantly impairs tissue healing.
- Refrain from alcohol
for
at
least one month post-treatment.